Diabetes
If you’ve ever wondered why your doctor talks about “A1c” or “insulin,” you’re not alone. Diabetes is common—and manageable—with the right tools and habits. What to know Diabetes is a condition where blood sugar (glucose) stays too high. This happens when your body doesn’t make enough insulin or...
Introduction Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose). Glucose is a vital source of energy for the body’s cells, but in diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. This...
Myths can get in the way of good care. Let’s separate fact from fiction so you can make confident choices. What to know Myth: “Eating sugar causes diabetes.” Fact: Type 1 is autoimmune; Type 2...
You may have heard stories of people “reversing” Type 2 diabetes. The more accurate term is remission—and yes, it’s possible for some people. What to know Definitions: Diabetes remission typically...
You can enjoy restaurants and celebrations without derailing your glucose. A few swaps and strategies go a long way. What to know Restaurant meals often have larger portions, refined carbs, and hidden...
Healthy pregnancy with diabetes is absolutely possible. Planning and close monitoring help protect both parent and baby. What to know Types in pregnancy: Preexisting diabetes: Type 1 or Type 2 present...
For older adults, the safest plan is often the simplest. The goals: fewer lows, fewer burdens, and more good days. What to know Individualize targets: Tighter goals if healthy/independent; looser...
From school lunches to sports and sleepovers, diabetes adds moving parts to family life. With a plan and practice, kids can thrive. What to know Types and onset: Type 1 is most common in kids; onset...
Your mouth and your blood sugar talk to each other. Healthier gums can mean better glucose—and vice versa. What to know Two‑way link: High glucose feeds gum bacteria, raising risk of gingivitis and...
You can eat well and exercise—and still see surprise glucose swings. Often the hidden culprits are short sleep and everyday stress. What to know Sleep and glucose: Short sleep (under ~7 hours) and...
A few minutes a day can prevent serious foot problems. Consistent foot care reduces ulcers, infections, and amputations. What to know Why feet are vulnerable: Reduced blood flow and nerve damage can...
Highs and lows happen—even with a great plan. Knowing your moves ahead of time keeps you safe and in control. What to know Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar): usually <70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Symptoms:...
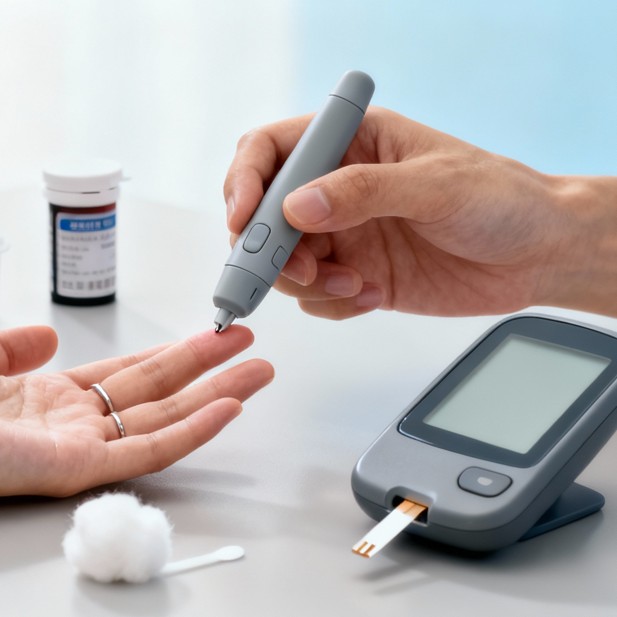
You can’t manage what you can’t see. Glucose monitoring turns guesswork into clear decisions you can act on. What to know Two main approaches: Finger-stick meters: spot checks. Inexpensive, accurate...
Insulin can feel intimidating—but with the right plan and a few routines, it becomes a reliable tool for steady blood sugar. What to know Why insulin: If oral/non‑insulin meds aren’t enough, or if...
There’s no one “best” diabetes medication—there’s the best one for you. Knowing the options helps you and your clinician build the right plan. What to know Goals of therapy: lower A1c, reduce...
Small, steady weight changes can meaningfully lower A1c, reduce medications, and boost energy—no extreme diets required. What to know Even 5–10% weight loss can improve blood sugar, blood pressure...
Exercise is one of the most powerful “medications” for diabetes—and it’s free. The right mix can lower A1c, improve energy, and protect your heart. What to know How it works: Activity helps muscles...
Mediterranean, plant‑based, low‑carb—so many plans, so little time. Which one actually works for blood sugar? Short answer: the one you can stick with. What to know Multiple eating patterns can...
Staring at your plate and wondering “how much is too much?” You’re not alone. A few simple frameworks can make meals stress‑free. What to know Three flexible approaches: Plate Method: visual...
Carbs aren’t the enemy—understanding which ones, how much, and how you pair them is the secret. What to know Carbohydrates raise blood sugar the most, but effects vary by type and portion. Glycemic...
You don’t need a “perfect” diet to manage diabetes. Small, steady changes to your plate can make a big difference. What to know Balanced meals help smooth blood sugar: Half plate non‑starchy veggies...
Type 1. Type 2. Same name, different stories. Understanding the difference helps you or a loved one get the right care. What to know The core difference: Type 1: Autoimmune disease. The immune system...
One in three adults has prediabetes—and most don’t know it. The good news: early changes can prevent or delay Type 2 diabetes. What to know Prediabetes means blood sugar is higher than normal but not...
