Male Pattern Baldness (MPB), also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common form of hair loss in men. It affects millions worldwide and can begin as early as the late teens or early twenties. While it is not a life-threatening condition, it can have a significant psychological impact, affecting self-esteem and confidence. This article explores the causes, available treatments, and coping strategies for male pattern baldness.
Causes of Male Pattern Baldness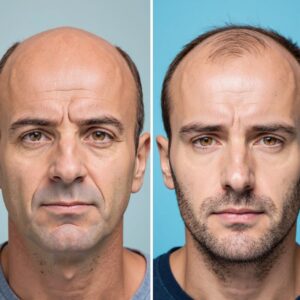
Male pattern baldness is primarily caused by a combination of genetic, hormonal, and age-related factors. The key contributors include:
1. Genetics
MPB is hereditary, meaning it often runs in families. If your father, grandfather, or other male relatives experienced hair loss, you are more likely to develop it. The genetic predisposition is linked to variations in the androgen receptor (AR) gene, which influences how hair follicles respond to hormones.
2. Hormonal Changes
The hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone, plays a central role in MPB. DHT binds to hair follicles, causing them to shrink over time. This process, known as follicular miniaturization, leads to thinner, shorter hair and eventually halts hair growth altogether.
3. Age
Hair loss becomes more common with age. By the age of 50, approximately 50% of men experience some degree of MPB. The aging process exacerbates the effects of DHT on hair follicles, making hair loss more pronounced.
4. Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
While genetics and hormones are the primary causes, certain lifestyle factors can accelerate hair loss. These include poor diet, high stress levels, smoking, and inadequate scalp care. However, these factors are secondary and typically exacerbate an existing predisposition to MPB.
Treatments for Male Pattern Baldness
Although there is no definitive cure for MPB, several treatments can slow its progression, stimulate hair regrowth, or improve the appearance of thinning hair. These treatments fall into three main categories: medical, surgical, and cosmetic.
1. Medical Treatments
Medical treatments are often the first line of defense against MPB. The most commonly used options include:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): An over-the-counter topical solution or foam that stimulates hair growth and slows hair loss. It is applied directly to the scalp and is most effective in the early stages of MPB.
- Finasteride (Propecia): A prescription oral medication that inhibits the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which converts testosterone into DHT. By reducing DHT levels, finasteride can slow hair loss and, in some cases, promote regrowth.
- Dutasteride: Similar to finasteride but more potent, dutasteride is sometimes prescribed off-label for MPB. It blocks both types of 5-alpha-reductase enzymes, leading to a more significant reduction in DHT levels.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): Devices such as laser combs or helmets use low-level lasers to stimulate hair follicles and improve hair density. While the evidence is mixed, some users report positive results.
2. Surgical Treatments
For men with advanced hair loss, surgical options can provide a more permanent solution:
- Hair Transplant Surgery: This involves harvesting hair follicles from areas of the scalp resistant to DHT (usually the back or sides) and transplanting them to balding areas. Techniques such as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) are commonly used.
- Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP): A non-invasive procedure that uses tattooing to create the appearance of a closely shaved head or fuller hair density.
3. Cosmetic Solutions
For those who prefer non-invasive options, cosmetic solutions can help improve the appearance of thinning hair:
- Hair Fibers: Keratin-based fibers that cling to existing hair, creating the illusion of thicker hair.
- Wigs and Hairpieces: High-quality wigs and hair systems can provide a natural-looking alternative for men with significant hair loss.
- Hairstyling Techniques: Strategic haircuts and styling can help conceal thinning areas.
Coping Strategies for Male Pattern Baldness
Dealing with hair loss can be emotionally challenging, but adopting healthy coping strategies can make the process easier. Here are some approaches to consider:
1. Acceptance
Embracing hair loss as a natural part of aging can be liberating. Many men choose to shave their heads or keep their hair very short, which can project confidence and eliminate the stress of trying to hide hair loss.
2. Focus on Overall Grooming
Maintaining a well-groomed appearance can shift attention away from hair loss. This includes growing facial hair, dressing well, and staying physically fit.
3. Seek Support
Talking to friends, family, or a therapist about your feelings can help you process the emotional impact of hair loss. Online forums and support groups can also provide a sense of community and shared experience.
4. Educate Yourself
Understanding the causes and treatments of MPB can empower you to make informed decisions. Researching options and consulting with a dermatologist or hair loss specialist can help you develop a personalized plan.
5. Practice Stress Management
Chronic stress can exacerbate hair loss. Incorporating stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies into your routine can improve both your mental health and overall well-being.
Conclusion
Male pattern baldness is a common condition that affects men of all ages and backgrounds. While it is primarily driven by genetics and hormones, various treatments and coping strategies can help manage its effects. Whether you choose to pursue medical or surgical interventions, embrace your natural look, or explore cosmetic solutions, the key is to find an approach that aligns with your personal preferences and lifestyle. Remember, hair loss does not define your worth or identity, and confidence comes from embracing who you are.
